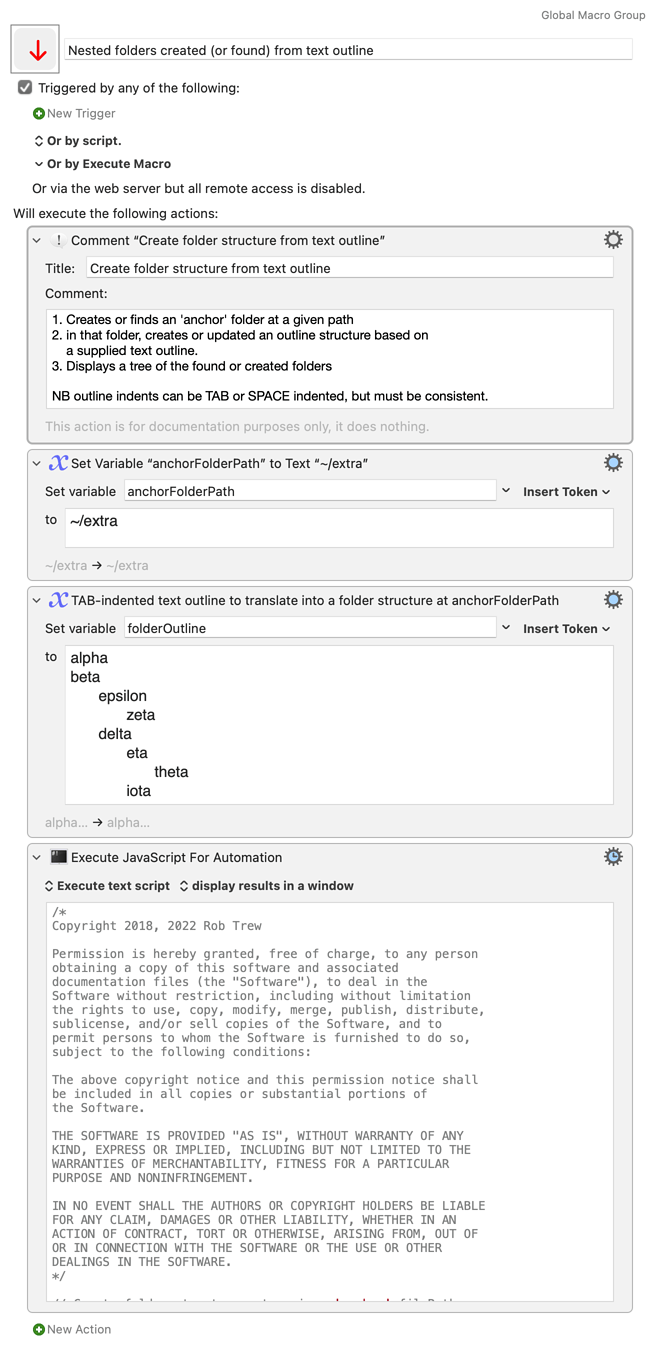
Updated code and simplified behaviour – simply displays a tree with full paths of the created (or found) nest of folders.
(Now makes no distinction, in the display, between 'found' and 'created' – some users may have found this confusing)
Nested folders created (or found) from text outline.kmmacros (14 KB)
Expand disclosure triangle to view JS Source
// Create a folder structure, at a given 'anchor' filePath,
// based on a supplied plain text outline.
// (must be consistently tab or 4-space indented)
// Ver 0.03
(() => {
"use strict";
// main :: IO String
const main = () => {
const
kme = Application("Keyboard Maestro Engine"),
kmVar = kme.getvariable;
return drawTree(
fmapTree(
compose(
either(x => x)(x => x),
createDirectoryIfMissingLR(true)
)
)(
filePathTree(kmVar("anchorFolderPath"))(
forestFromIndentedLines(
indentLevelsFromLines(
lines(kmVar("folderOutline"))
)
)
)
)
);
};
// ------------ TREES FROM INDENTED TEXT -------------
// forestFromIndentedLines :: [(Int, String)] ->
// [Tree {text:String, body:Int}]
const forestFromIndentedLines = tuples => {
const go = xs =>
0 < xs.length ? (() => {
// First line and its sub-tree,
const [depth, body] = xs[0],
[tree, rest] = span(x => depth < x[0])(
xs.slice(1)
);
return [
Node({
text: body,
level: depth
})(go(tree))
]
// followed by the rest.
.concat(go(rest));
})() : [];
return go(tuples);
};
// indentLevelsFromLines :: [String] -> [(Int, String)]
const indentLevelsFromLines = xs => {
const
pairs = xs.map(
x => bimap(
cs => cs.length
)(
cs => cs.join("")
)(
span(isSpace)([...x])
)
),
indentUnit = pairs.reduce(
(a, [i]) => 0 < i ? (
i < a ? i : a
) : a,
Infinity
);
return [Infinity, 0].includes(indentUnit) ? (
pairs
) : pairs.map(first(n => n / indentUnit));
};
// ---------------- GENERIC FUNCTIONS ----------------
// Left :: a -> Either a b
const Left = x => ({
type: "Either",
Left: x
});
// Node :: a -> [Tree a] -> Tree a
const Node = v =>
// Constructor for a Tree node which connects a
// value of some kind to a list of zero or
// more child trees.
xs => ({
type: "Node",
root: v,
nest: xs || []
});
// Right :: b -> Either a b
const Right = x => ({
type: "Either",
Right: x
});
// Tuple (,) :: a -> b -> (a, b)
const Tuple = a =>
// A pair of values, possibly of
// different types.
b => ({
type: "Tuple",
"0": a,
"1": b,
length: 2,
*[Symbol.iterator]() {
for (const k in this) {
if (!isNaN(k)) {
yield this[k];
}
}
}
});
// bimap :: (a -> b) -> (c -> d) -> (a, c) -> (b, d)
const bimap = f =>
// Tuple instance of bimap.
// A tuple of the application of f and g to the
// first and second values respectively.
g => tpl => Tuple(f(tpl[0]))(
g(tpl[1])
);
// compose (<<<) :: (b -> c) -> (a -> b) -> a -> c
const compose = (...fs) =>
// A function defined by the right-to-left
// composition of all the functions in fs.
fs.reduce(
(f, g) => x => f(g(x)),
x => x
);
// createDirectoryIfMissingLR :: Bool -> FilePath
// -> Either String FilePath
const createDirectoryIfMissingLR = blnParents =>
dirPath => {
const fp = filePath(dirPath);
return doesPathExist(fp) ? (
Right(fp)
) : (() => {
const
e = $(),
blnOK = $.NSFileManager
.defaultManager[
"createDirectoryAtPath" + (
"WithIntermediateDirectories"
) + "AttributesError"
](fp, blnParents, void 0, e);
return blnOK ? (
Right(fp)
) : Left(e.localizedDescription);
})();
};
// doesPathExist :: FilePath -> IO Bool
const doesPathExist = fp =>
$.NSFileManager.defaultManager
.fileExistsAtPath(
$(fp).stringByStandardizingPath
);
// draw :: Tree String -> [String]
const draw = node => {
// shift :: String -> String -> [String] -> [String]
const shifted = (first, other, xs) => (
[first].concat(
Array.from({
length: xs.length - 1
}, () => other)
).map(
(y, i) => y.concat(xs[i])
)
);
// drawSubTrees :: [Tree String] -> [String]
const drawSubTrees = xs => {
const lng = xs.length;
return 0 < lng ? (
1 < lng ? (
["│"].concat(
shifted("├─ ", "│ ", draw(xs[0]))
)
).concat(
drawSubTrees(xs.slice(1))
) : ["│"].concat(
shifted("└─ ", " ", draw(xs[0]))
)
) : [];
};
return node.root.split("\n").concat(
drawSubTrees(node.nest)
);
};
// drawTree :: Tree String -> String
const drawTree = tree =>
draw(tree).join("\n");
// either :: (a -> c) -> (b -> c) -> Either a b -> c
const either = fl =>
// Application of the function fl to the
// contents of any Left value in e, or
// the application of fr to its Right value.
fr => e => "Left" in e ? (
fl(e.Left)
) : fr(e.Right);
// filePath :: String -> FilePath
const filePath = s =>
// The given file path with any tilde expanded
// to the full user directory path.
ObjC.unwrap(
ObjC.wrap(s)
.stringByStandardizingPath
);
// filePathTree :: filePath -> [Tree String] -> Tree FilePath
const filePathTree = fpAnchor => trees => {
const go = fp => tree => {
const path = `${fp}/${tree.root.text}`;
return Node(path)(
tree.nest.map(go(path))
);
};
return Node(fpAnchor)(
trees.map(go(fpAnchor))
);
};
// first :: (a -> b) -> ((a, c) -> (b, c))
const first = f =>
// A simple function lifted to one which applies
// to a tuple, transforming only its first item.
([x, y]) => [f(x), y];
// fmapTree :: (a -> b) -> Tree a -> Tree b
const fmapTree = f => {
// A new tree. The result of a
// structure-preserving application of f
// to each root in the existing tree.
const go = t => Node(
f(root(t))
)(
nest(t).map(go)
);
return go;
};
// isSpace :: Char -> Bool
const isSpace = c =>
// True if c is a white space character.
(/\s/u).test(c);
// lines :: String -> [String]
const lines = s =>
// A list of strings derived from a single string
// which is delimited by \n or by \r\n or \r.
Boolean(s.length) ? (
s.split(/\r\n|\n|\r/u)
) : [];
// nest :: Tree a -> [a]
const nest = tree => {
// Allowing for lazy (on-demand) evaluation.
// If the nest turns out to be a function –
// rather than a list – that function is applied
// here to the root, and returns a list.
const xs = tree.nest;
return "function" !== typeof xs ? (
xs
) : xs(root(tree));
};
// root :: Tree a -> a
const root = tree =>
// The value attached to a tree node.
tree.root;
// span :: (a -> Bool) -> [a] -> ([a], [a])
const span = p =>
// Longest prefix of xs consisting of elements which
// all satisfy p, tupled with the remainder of xs.
xs => {
const i = xs.findIndex(x => !p(x));
return -1 !== i ? (
Tuple(xs.slice(0, i))(
xs.slice(i)
)
) : Tuple(xs)([]);
};
// MAIN ---
return main();
})();