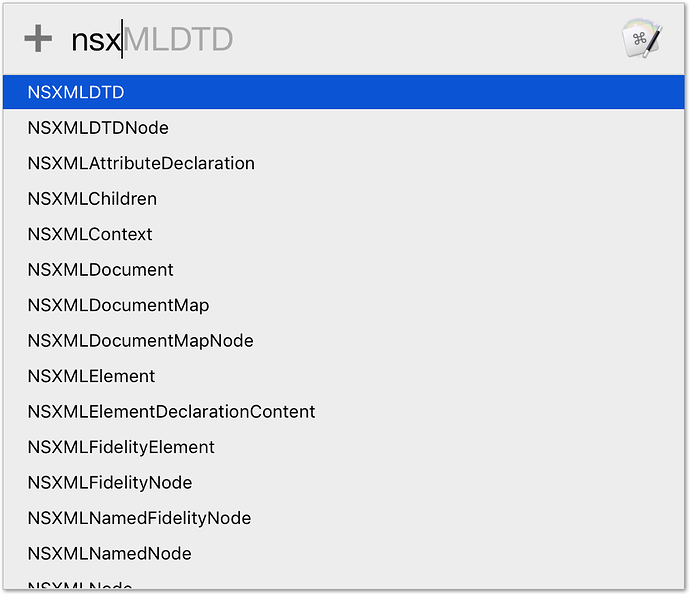
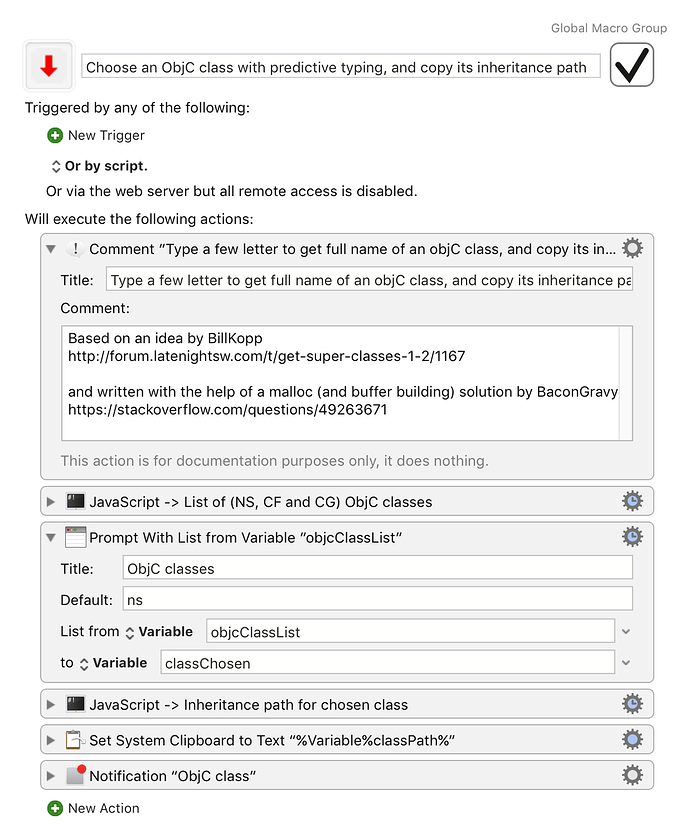
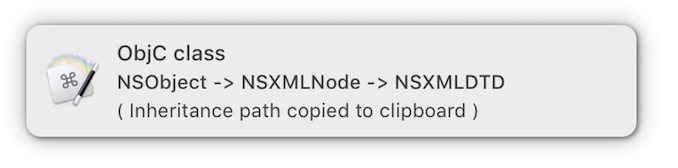
Provides inheritance paths like:
NSObject -> NSAttributedString -> NSMutableAttributedString -> NSTextStorage -> NSSubTextStorage
NSObject -> NSResponder -> NSView -> _NSKeyLoopSplicingContainerView -> NSTabBarViewButton -> NSTabButton
NSObject -> NSBinder -> NSEditorBinder -> NSObjectDetailBinder -> NSArrayDetailBinder -> NSTreeDetailBinder
etc.
for a chosen class name.
To extend or restrict the list of ObjC classes listed, adjust the JavaScript source below (for the first of the two Execute a JXA actions in the macro - the second action derives the inheritance path of the chosen class)
Choose an ObjC class with predictive typing, and copy its inheritance path.kmmacros (29.0 KB)
JavaScript for Automation source:
(1 of 2) List of (NS, CF and CG) ObjC classes
(() => {
'use strict';
['AppKit', 'Quartz', 'Carbon']
.forEach(k => ObjC.import(k));
// prefixes :: [String]
const prefixes = ['NS','CF', 'CG'];
// main :: () -> String
const main = () => {
const xs = objcClassNames();
return unlines(concat(
groupBy(
(a, b) => a.slice(0, 2) === b.slice(0, 2),
xs.sort()
)
.filter(x => prefixes.includes(x[0].slice(0, 2)))
));
};
// OBJC CLASS NAMES -------------------------------------------------------
// objcClassNames :: () -> [String]
const objcClassNames = () => {
// See: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/49263671
ObjC.bindFunction('objc_getClassList', ['int', ['void**', 'int']]);
ObjC.bindFunction('class_getName', ['char *', ['void*']]);
ObjC.bindFunction('malloc', ['void**', ['int']]);
const
intClasses = $.objc_getClassList(undefined, 0),
classes = $.malloc(8 * intClasses);
return (
$.objc_getClassList(classes, intClasses),
Array.from({
length: intClasses
}, (_, i) => $.class_getName(classes[i]))
);
};
// GENERICS --------------------------------------------------------------
// concat :: [[a]] -> [a]
// concat :: [String] -> String
const concat = xs =>
xs.length > 0 ? (() => {
const unit = typeof xs[0] === 'string' ? '' : [];
return unit.concat.apply(unit, xs);
})() : [];
// group :: Eq a => [a] -> [[a]]
const group = xs => groupBy((a, b) => a === b, xs);
// Typical usage: groupBy(on(eq, f), xs)
// groupBy :: (a -> a -> Bool) -> [a] -> [[a]]
const groupBy = (f, xs) => {
const dct = xs.slice(1)
.reduce((a, x) => {
const h = a.active.length > 0 ? a.active[0] : undefined;
return h !== undefined && f(h, x) ? {
active: a.active.concat([x]),
sofar: a.sofar
} : {
active: [x],
sofar: a.sofar.concat([a.active])
};
}, {
active: xs.length > 0 ? [xs[0]] : [],
sofar: []
});
return dct.sofar.concat(dct.active.length > 0 ? [dct.active] : []);
};
// showJSON :: a -> String
const showJSON = x => JSON.stringify(x, null, 2);
// take :: Int -> [a] -> [a]
const take = (n, xs) => xs.slice(0, n);
// unlines :: [String] -> String
const unlines = xs => xs.join('\n');
// MAIN ------------------------------------------------------------------
return main();
})();
(2 of 2) Inheritance path of chosen class
(() => {
'use strict';
// main :: () -> String
const main = () =>
intercalate(' -> ', classPath(
Application('Keyboard Maestro Engine')
.getvariable('classChosen')
));
// OBJC CLASSES ---------------------------------------------------------
// className :: NSObject -> String
const className = anyClass =>
ObjC.unwrap($.NSStringFromClass(anyClass));
// classPath :: String -> [String]
const classPath = strClassName =>
strClassName.includes('NSLeafProxy') ? (
['.superClass not defined for NSLeafProxy']
) : (() => {
try {
const childClass = $.NSClassFromString(strClassName);
return ObjC.unwrap(childClass) === undefined ? (
[]
) : ['NSObject'].concat(
// UNFOLDR builds a list from a seed value.
unfoldr(parentClass, childClass)
);
} catch (e) {
return ['.superClass not defined for ' + strClassName];
}
})();
// parentClass :: NSObject -> Maybe (String, NSObject)
const parentClass = anyClass => {
const strName = className(anyClass);
return 'NSObject' === strName ? (
Nothing()
) : Just(Tuple(strName, anyClass.superclass));
};
// GENERIC FUNCTIONS -----------------------------------------------------
// Just :: a -> Just a
const Just = x => ({
type: 'Maybe',
Nothing: false,
Just: x
});
// Nothing :: () -> Nothing
const Nothing = () => ({
type: 'Maybe',
Nothing: true,
});
// Tuple (,) :: a -> b -> (a, b)
const Tuple = (a, b) => ({
type: 'Tuple',
'0': a,
'1': b
});
// concat :: [[a]] -> [a]
// concat :: [String] -> String
const concat = xs =>
xs.length > 0 ? (() => {
const unit = typeof xs[0] === 'string' ? '' : [];
return unit.concat.apply(unit, xs);
})() : [];
// intercalate :: [a] -> [[a]] -> [a]
// intercalate :: String -> [String] -> String
const intercalate = (sep, xs) =>
xs.length > 0 && typeof sep === 'string' &&
typeof xs[0] === 'string' ? (
xs.join(sep)
) : concat(intersperse(sep, xs));
// intersperse(0, [1,2,3]) -> [1, 0, 2, 0, 3]
// intersperse :: Char -> String -> String
// intersperse :: a -> [a] -> [a]
const intersperse = (sep, xs) => {
const bool = (typeof xs)[0] === 's';
return xs.length > 1 ? (
(bool ? concat : x => x)(
(bool ? (
xs.split('')
) : xs)
.slice(1)
.reduce((a, x) => a.concat([sep, x]), [xs[0]])
)) : xs;
};
// The 'unfoldr' function is a \`dual\' to 'foldr': while 'foldr'
// reduces a list to a summary value, 'unfoldr' builds a list from
// a seed value. The function takes the element and returns 'Nothing'
// if it is done producing the list or returns 'Just' @(a,b)@, in which
// case, @a@ is a prepended to the list and @b@ is used as the next
// element in a recursive call.
//
// unfoldr(b => b === 0 ? Nothing() : Just(Tuple(b, b - 1)), 10);
// --> [10,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1]
// (x => Maybe [value, remainder] -> initial value -> values
// unfoldr :: (b -> Maybe (a, b)) -> b -> [a]
const unfoldr = (f, v) => {
let xs = [];
return (
until(
mb => mb.Nothing,
mb => (
xs.push(mb.Just[0]),
f(mb.Just[1])
), Just(Tuple(v, v))
),
xs.slice(1)
);
};
// until :: (a -> Bool) -> (a -> a) -> a -> a
const until = (p, f, x) => {
let v = x;
while (!p(v)) v = f(v);
return v;
};
// MAIN --------------------------------------------------------------
return main();
})();