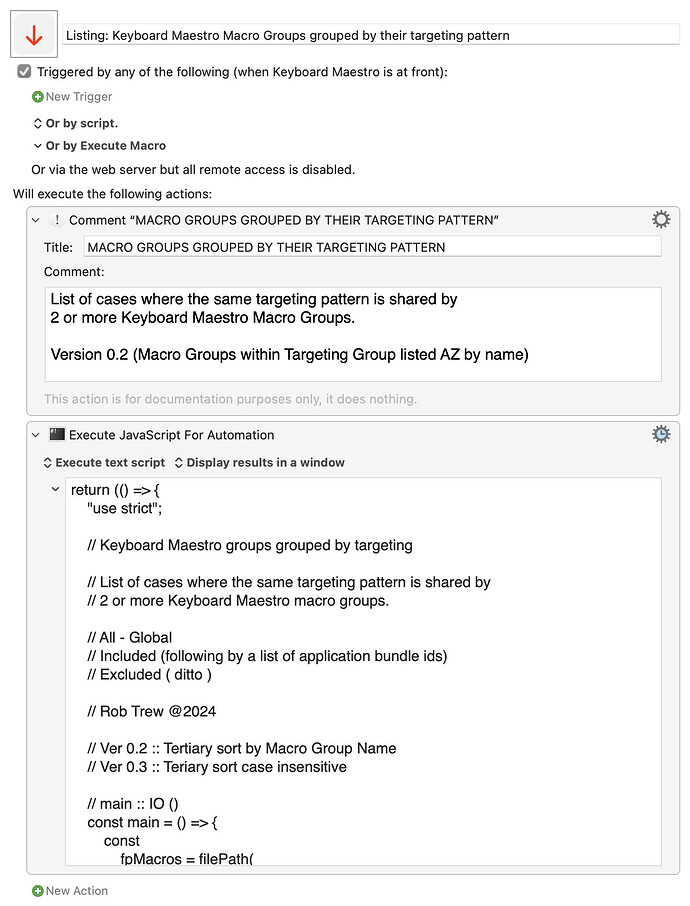
A list of any cases where 2 or more Keyboard Maestro Macro groups have the same targeting.
Global macro groups are listed under the heading All.
Others under the headings Included or Excluded, followed by a particular list of one or more application bundle identifiers.
In my case, for example, I find that:
- I seem to have 50 globally-targeted macro groups,
- 3 different macro groups which all target Safari,
- another three macro groups which all target only the Keyboard Maestro Editor
- two macro groups which both define keystrokes for ALL applications excluding Taskpaper
- two puzzlingly separated groups which both target Mellel,
etc etc ...
Listing- Keyboard Maestro Macro Groups grouped by their targeting pattern.kmmacros (14 KB)
Expand disclosure triangle to view JS source
return (() => {
"use strict";
// Keyboard Maestro groups grouped by targeting
// List of cases where the same targeting pattern is shared by
// 2 or more Keyboard Maestro macro groups.
// All - Global
// Included (following by a list of application bundle ids)
// Excluded ( ditto )
// Rob Trew @2024
// Ver 0.2 :: Tertiary sort by Macro Group Name
// Ver 0.3 :: Teriary sort case insensitive
// main :: IO ()
const main = () => {
const
fpMacros = filePath(
combine(
"~/Library/Application Support"
)(
"Keyboard Maestro/Keyboard Maestro Macros.plist"
)
);
return either(
alert("Macros grouped by targeting")
)(
groupTargetingReport
)(
doesFileExist(fpMacros)
? fmapLR(
macroGroupsGroupedByTarget
)(
jsoFromPlistPathLR(fpMacros)
)
: Left(`Not found at path: "${fpMacros}"`)
);
};
// targetGroups :: [[(Name, Targeting)]] -> String
const groupTargetingReport = targetGroups =>
// List of cases where a targeting pattern
// is shared by 2 or more macro groups.
unlines(
targetGroups.flatMap(gp => 1 < gp.length
? [
unlines([
`${gp.length} Groups:`,
unlines(
gp[0][1].flatMap(
x => 0 < x.length
? [`\t${x.replaceAll("\n", "\n\t")}`]
: []
)
),
unlines(gp.map(pair => `\t\t- ${pair[0]}`))
])
]
: []
)
);
// macroGroupsGroupedByTarget :: Dict -> [[(Name, Targeting)]]
const macroGroupsGroupedByTarget = dict => {
const groups = dict.MacroGroups;
return sortBy(
flip(
comparing(gp => gp.length)
)
)(
groupOn(
// String of sorted bundleIDs,
// within target type groupings.
x => x[1][1]
)(
sortBy(
targetTypeThenBundlesThenName()
)(
zipWith(Tuple)(
groups.map(g => g.Name)
)(
groups.map(g => g.Targeting)
)
.flatMap(
pair => pair[1]
? [second(targetDetails)(pair)]
: []
)
)
)
);
};
// nAryCompare :: [(a -> b)] -> a -> a -> Ordering
const nAryCompare = fs =>
fs.slice(1).reduce(
(a, f) => mappendComparing(a)(comparing(f)),
comparing(fs[0])
);
// targetTypeThenBundlesThenName ::
// (String, (String, String)) ->
// (String, (String, String)) - Ordering
const targetTypeThenBundlesThenName = () =>
nAryCompare([
// Target type
x => x[1][0],
// Application bundle ids string
x => x[1][1],
// Macro Group Name
x => toLower(x[0])
]);
// targetDetails :: Dict -> (String, String)
const targetDetails = targeting =>
[
targeting.Targeting,
targeting.TargetingApps
.map(x => x.BundleIdentifier)
.sort()
.join("\n")
];
// jsoFromPlistPathLR :: PLIST FilePath ->
// Either String Dict
const jsoFromPlistPathLR = fpPlist => {
try {
const
dict = ObjC.deepUnwrap(
$.NSDictionary.dictionaryWithContentsOfURL(
$.NSURL.fileURLWithPath(fpPlist)
)
);
return undefined !== dict
? Right(dict)
: Left(`Could not be read as .plist: "${fpPlist}"`)
} catch (e) {
return Left(e.message);
}
};
// ----------------------- JXA -----------------------
// alert :: String => String -> IO String
const alert = title =>
s => {
const sa = Object.assign(
Application("System Events"), {
includeStandardAdditions: true
});
return (
sa.activate(),
sa.displayDialog(s, {
withTitle: title,
buttons: ["OK"],
defaultButton: "OK"
}),
s
);
};
// --------------------- GENERIC ---------------------
// Left :: a -> Either a b
const Left = x => ({
type: "Either",
Left: x
});
// Right :: b -> Either a b
const Right = x => ({
type: "Either",
Right: x
});
// Tuple (,) :: a -> b -> (a, b)
const Tuple = a =>
// A pair of values, possibly of
// different types.
b => ({
type: "Tuple",
"0": a,
"1": b,
length: 2,
*[Symbol.iterator]() {
for (const k in this) {
if (!isNaN(k)) {
yield this[k];
}
}
}
});
// combine (</>) :: FilePath -> FilePath -> FilePath
const combine = fp =>
// The concatenation of two filePath segments,
// without omission or duplication of "/".
fp1 => Boolean(fp) && Boolean(fp1)
? "/" === fp1.slice(0, 1)
? fp1
: "/" === fp.slice(-1)
? fp + fp1
: `${fp}/${fp1}`
: (fp + fp1);
// comparing :: Ord a => (b -> a) -> b -> b -> Ordering
const comparing = f =>
// The ordering of f(x) and f(y) as a value
// drawn from {-1, 0, 1}, representing {LT, EQ, GT}.
x => y => {
const
a = f(x),
b = f(y);
return a < b
? -1
: a > b
? 1
: 0;
};
// doesFileExist :: FilePath -> IO Bool
const doesFileExist = fp => {
const ref = Ref();
return $.NSFileManager
.defaultManager
.fileExistsAtPathIsDirectory(
$(fp).stringByStandardizingPath,
ref
) && !ref[0];
};
// either :: (a -> c) -> (b -> c) -> Either a b -> c
const either = fl =>
// Application of the function fl to the
// contents of any Left value in e, or
// the application of fr to its Right value.
fr => e => "Left" in e
? fl(e.Left)
: fr(e.Right);
// fmapLR (<$>) :: (b -> c) -> Either a b -> Either a c
const fmapLR = f =>
// Either f mapped into the contents of any Right
// value in e, or e unchanged if it is a Left value.
e => "Left" in e
? e
: Right(f(e.Right));
// flip :: (a -> b -> c) -> b -> a -> c
const flip = op =>
// The binary function op with
// its arguments reversed.
1 !== op.length
? (a, b) => op(b, a)
: (a => b => op(b)(a));
// filePath :: String -> FilePath
const filePath = s =>
// The given file path with any tilde expanded
// to the full user directory path.
ObjC.unwrap(
$(s).stringByStandardizingPath
);
// groupBy :: (a -> a -> Bool) -> [a] -> [[a]]
const groupBy = eqOp =>
// A list of lists, each containing only elements
// equal under the given equality operator, such
// that the concatenation of these lists is xs.
xs => 0 < xs.length
? (() => {
const [h, ...t] = xs;
const [groups, g] = t.reduce(
([gs, a], x) => eqOp(a[0])(x)
? [gs, [...a, x]]
: [[...gs, a], [x]],
[[], [h]]
);
return [...groups, g];
})()
: [];
// groupOn :: (a -> b) -> [a] -> [[a]]
const groupOn = f =>
// A list of lists, each containing only elements
// which return equal values for f,
// such that the concatenation of these lists is xs.
xs => 0 < xs.length
? groupBy(a => b => a[0] === b[0])(
xs.map(x => [f(x), x])
)
.map(gp => gp.map(ab => ab[1]))
: [];
// mappendComparing (<>) :: (a -> a -> Bool)
// (a -> a -> Bool) -> (a -> a -> Bool)
const mappendComparing = cmp =>
cmp1 => a => b => {
const x = cmp(a)(b);
return 0 !== x
? x
: cmp1(a)(b);
};
// second :: (a -> b) -> ((c, a) -> (c, b))
const second = f =>
// A function over a simple value lifted
// to a function over a tuple.
// f (a, b) -> (a, f(b))
xy => Tuple(
xy[0]
)(
f(xy[1])
);
// sortBy :: (a -> a -> Ordering) -> [a] -> [a]
const sortBy = f =>
// A copy of xs sorted by the comparator function f.
xs => xs.slice()
.sort((a, b) => f(a)(b));
// toLower :: String -> String
const toLower = s =>
// Lower-case version of string.
s.toLocaleLowerCase();
// unlines :: [String] -> String
const unlines = xs =>
// A single string formed by the intercalation
// of a list of strings with the newline character.
xs.join("\n");
// zipWith :: (a -> a -> b) -> [a] -> [b]
const zipWith = f =>
// A list with the length of the shorter of
// xs and ys, defined by zipping with a
// custom function, rather than with the
// default tuple constructor.
xs => ys => xs.slice(
0, Math.min(xs.length, ys.length)
)
.map((x, i) => f(x)(ys[i]));
return main();
})();
Partly inspired by discussion of scope for consolidating macro groups in this thread: