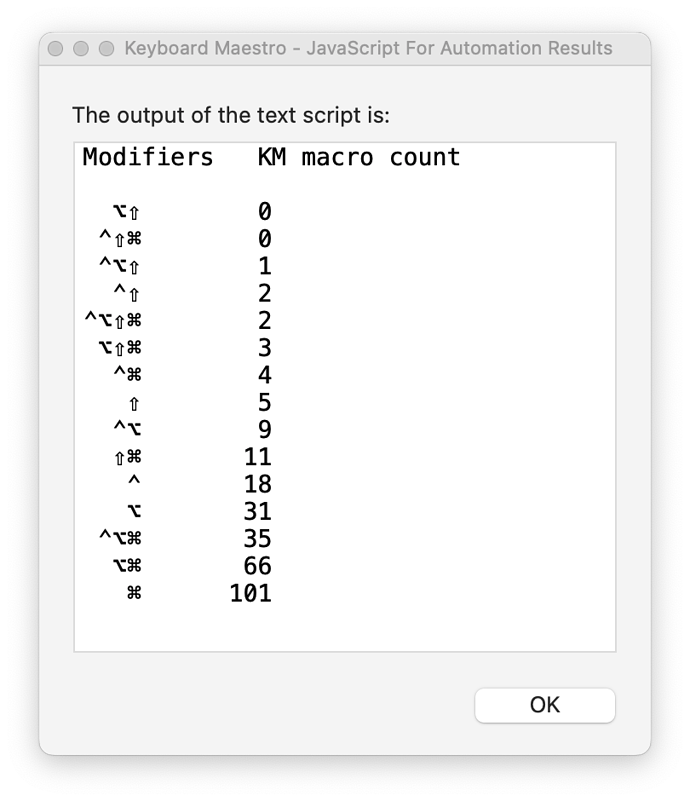
Easy to forget, when choosing a macro-launching hot-key, that there are 15 possible combinations of modifier keys:
⌃, ⌥, ⇧, ⌘, ⌃⌥, ⌃⇧, ⌃⌘, ⌥⇧, ⌥⌘, ⇧⌘, ⌃⌥⇧, ⌃⌥⌘, ⌃⇧⌘, ⌥⇧⌘, ⌃⌥⇧⌘
Which ones am I overlooking or under-using ?
Here's a macro which shows the stats of your Keyboard Maestro hot-key modifier usage.
In my case for example, ⌥⇧ and ⌃⇧⌘ both seem to be blind spots, and some others are not much used:
Underused key combinations ? KM hot-key modifier stats.kmmacros (9.8 KB)
Expand disclosure triangle to view JS Source
(() => {
"use strict";
// Listing of Keyboard Maestro hot-key
// trigger modifier usage frequencies.
// Rob Trew @2022
const main = () => {
const
modifiers = modifierCombinations(),
frequencies = kmModFrequencies()
.filter(ab => Boolean(ab[0])),
usedModifiers = frequencies.map(fst),
unused = modifiers.filter(
m => !usedModifiers.includes(m)
);
return ["Modifiers KM macro count\n"].concat([
...unused.map(s => [s, 0]),
...frequencies
]
.map(
([k, n]) => [
`${k.padStart(4, " ")}`,
`${n.toString().padStart(4, " ")}`
]
.join(" ")
)
)
.join("\n");
};
// ------------------ MODIFER KEYS -------------------
// kmModFrequencies :: IO () -> [(String, Int)]
const kmModFrequencies = () => {
const
km = Application("Keyboard Maestro"),
rgxMod = /[⇧⌃⌥⌘]/u;
return sortOn(length)(
groupBy(
on(eq)(fst)
)(
sortBy(
mappendComparing(
comparing(fst)
)(
comparing(snd)
)
)(
km.macros.triggers.where({
description: {
_beginsWith: "The Hot Key"
}
})
.description()
.flat()
.map(
s => both(cs => cs.join(""))(
span(
c => (rgxMod).test(c)
)([...s.slice(12, -11)])
)
)
)
)
).map(x => [fst(fst(x)), x.length]);
};
const modifier = {
"⌃": "ctrl",
"⌥": "opt",
"⇧": "shift",
"⌘": "cmd"
};
// modifierCombinations :: () -> [String]
const modifierCombinations = () => {
const ks = Object.keys(modifier);
return enumFromTo(1)(4)
.flatMap(flip(combinations)(ks))
.map(cs => cs.join(""));
};
// --------------------- GENERIC ---------------------
// Tuple (,) :: a -> b -> (a, b)
const Tuple = a =>
// A pair of values, possibly of
// different types.
b => ({
type: "Tuple",
"0": a,
"1": b,
length: 2,
*[Symbol.iterator]() {
for (const k in this) {
if (!isNaN(k)) {
yield this[k];
}
}
}
});
// both :: (a -> b) -> (a, a) -> (b, b)
const both = f =>
// A tuple obtained by applying f to both values
// in the given tuple.
([a, b]) => Tuple(
f(a)
)(
f(b)
);
// combinations :: Int -> [a] -> [[a]]
const combinations = n =>
// Combinations, without repetition,
// of n items drawn from xs.
xs => {
const go = (m, ys) =>
1 > m ? [
[]
] : 0 === ys.length ? (
[]
) : ((h, tail) => go(m - 1, tail)
.map(t => [h].concat(t))
.concat(go(m, tail))
)(ys[0], ys.slice(1));
return (go)(n, xs);
};
// comparing :: (a -> b) -> (a -> a -> Ordering)
const comparing = f =>
// The ordering of f(x) and f(y) as a value
// drawn from {-1, 0, 1}, representing {LT, EQ, GT}.
x => y => {
const
a = f(x),
b = f(y);
return a < b ? -1 : (a > b ? 1 : 0);
};
// enumFromTo :: Int -> Int -> [Int]
const enumFromTo = m =>
n => Array.from({
length: 1 + n - m
}, (_, i) => m + i);
// eq (==) :: Eq a => a -> a -> Bool
const eq = a =>
// True when a and b are equivalent in the terms
// defined below for their shared data type.
b => a === b;
// flip :: (a -> b -> c) -> b -> a -> c
const flip = op =>
// The binary function op with
// its arguments reversed.
1 !== op.length ? (
(a, b) => op(b, a)
) : (a => b => op(b)(a));
// fst :: (a, b) -> a
const fst = tpl =>
// First member of a pair.
tpl[0];
// groupBy :: (a -> a -> Bool) -> [a] -> [[a]]
const groupBy = eqOp =>
// A list of lists, each containing only elements
// equal under the given equality operator,
// such that the concatenation of these lists is xs.
xs => Boolean(xs.length) ? (() => {
const [h, ...t] = xs;
const [groups, g] = t.reduce(
([gs, a], x) => eqOp(x)(a[0]) ? (
Tuple(gs)([...a, x])
) : Tuple([...gs, a])([x]),
Tuple([])([h])
);
return [...groups, g];
})() : [];
// length :: [a] -> Int
const length = xs =>
// Returns Infinity over objects without finite
// length. This enables zip and zipWith to choose
// the shorter argument when one is non-finite,
// like cycle, repeat etc
"GeneratorFunction" !== xs.constructor
.constructor.name ? (
xs.length
) : Infinity;
// mappendComparing (<>) :: (a -> a -> Bool)
// (a -> a -> Bool) -> (a -> a -> Bool)
const mappendComparing = cmp =>
cmp1 => a => b => {
const x = cmp(a)(b);
return 0 !== x ? (
x
) : cmp1(a)(b);
};
// on :: (b -> b -> c) -> (a -> b) -> a -> a -> c
const on = f =>
// e.g. groupBy(on(eq)(length))
g => a => b => f(g(a))(g(b));
// snd :: (a, b) -> b
const snd = tpl =>
// Second member of a pair.
tpl[1];
// sortBy :: (a -> a -> Ordering) -> [a] -> [a]
const sortBy = f =>
// A copy of xs sorted by the comparator function f.
xs => xs.slice()
.sort((a, b) => f(a)(b));
// sortOn :: Ord b => (a -> b) -> [a] -> [a]
const sortOn = f =>
// Equivalent to sortBy(comparing(f)), but with f(x)
// evaluated only once for each x in xs.
// ('Schwartzian' decorate-sort-undecorate).
xs => sortBy(
comparing(x => x[0])
)(
xs.map(x => [f(x), x])
)
.map(x => x[1]);
// span :: (a -> Bool) -> [a] -> ([a], [a])
const span = p =>
// Longest prefix of xs consisting of elements which
// all satisfy p, tupled with the remainder of xs.
xs => {
const i = xs.findIndex(x => !p(x));
return -1 !== i ? (
Tuple(xs.slice(0, i))(
xs.slice(i)
)
) : Tuple(xs)([]);
};
// MAIN ---
return main();
})();